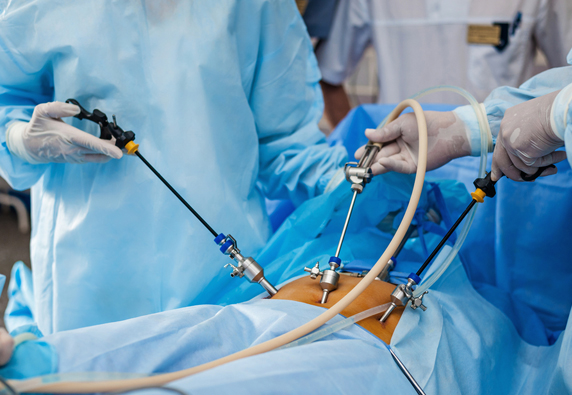
Key Hole of Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery involves making small incisions (referred to as keyhole incisions) through which specialized surgical instruments and a camera (laparoscope) are inserted into the body. This allows surgeons to perform various surgical procedures with less trauma to the surrounding tissues compared to traditional open surgery.
Here are some key points about laparoscopic or minimally invasive surgery:
- Small Incisions: Instead of a large single incision used in open surgery, laparoscopic surgery involves making several small incisions, typically less than one centimeter in size.
- Camera and Instruments: A laparoscope, which is a thin tube with a camera and light source attached to it, is inserted through one of the keyhole incisions to provide a magnified view of the internal organs on a video monitor. Specialized surgical instruments are inserted through the other incisions to perform the procedure under the guidance of the camera.
- Less Trauma: Minimally invasive surgery is associated with less trauma to the surrounding tissues, reduced blood loss, and typically leads to faster recovery times, shorter hospital stays, and less postoperative pain compared to open surgery.
- Various Procedures: Laparoscopic surgery can be used to perform a wide range of surgical procedures across different medical specialties, including gynaecology, urology, general surgery, orthopaedics, and more. Common procedures include gallbladder removal (laparoscopic cholecystectomy), appendectomy, hernia repair, and hysterectomy.
- Benefits: The benefits of laparoscopic surgery include smaller scars, reduced risk of infection, decreased postoperative pain, quicker return to normal activities, and improved cosmetic outcomes compared to traditional open surgery.